|
BACITRACIN ZINC |
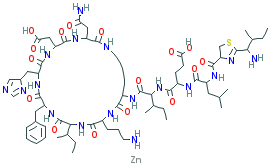
| Synonyms. Bacitracin zinc; Cortisporin; Neo-Polycin; Neobacimyx; Neosporin; Polysporin; 4-((2-((2-(1-amino-2-methylbutyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazole-4-carbonyl)amino)-4-methylpentanoyl) amino)-5-((1-((3-(2- amino-2-oxoethyl)-18-(3-aminopropyl)-12-benzyl-15-butan-2-yl-6- (carboxymethyl)- 9-(4H-imidazol-4-ylmethyl)-2,5,8,11,14,17,20-heptaoxo-1, 4,7,10,13,16, 19-heptazacyclo pentacos-21-yl)amino)-3-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl)amino)-5- oxopentanoic acid zinc salt; Bacitracina; Bacitracine; Bacitracinum; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION | |
|
CAS RN |
1405-89-6, 1405-87-4 (parent) |
|
EINECS RN |
215-787-8 |
|
FORMULA |
C66H101N17O16SZn |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
1486.07 |
|
H.S CODE |
2941.90.1050 |
|
SMILES |
[Zn].CC[C@@H](C)[C@@H](N)C1=N[C@@H](CS1)C(=O)N[C@@H] (CC(C)C) C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C (=O)N[C@@ H]1 CCCC NC(=O)[C@@H](CC(N)=O)NC(=O)[C@@H](CC(O)= O)NC(=O )[ C @ @H](C[C@@H]2C=NC=N2)NC(=O)[C@@H](Cc2ccccc2) NC(=O)[ C@ @H](NC(=O)[C@@H](CCCN)NC1=O)[C@@H](C)CC |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Antibacterial, Anti-Infective, Polypeptide antibiotic |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
A complex of cyclic peptide antibiotics produced by the Tracy-I strain of Bacillus subtilis. The commercial preparation is a mixture of at least nine bacitracins with bacitracin A as the major constituent. It is used topically to treat open infections such as infected eczema and infected dermal ulcers. (From Goodman and Gilman, The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th ed, p1140)
TSCA Definition 2008: A complex combination of polypeptides produced by the metabolic processes of Bacillus subtilis and licheniformis. EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 006309; Other RN: 1405-75-0, 8028-08-8, 8028-35-1, 8058-81-9, 11031-59-7, 73560-74-4, 92528-87-5, 12640-37-8, 60454-67-3 |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
|
PHYSICAL STATE. |
white crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
250 C (Decomposes) |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
5.1 g/l |
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | 6.55 g/l methanol, 2.0 g/l ethanol |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
log P(octanol-water) |
-0.91 |
|
VAPOR PRESSURE |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION TEMP |
|
| pH |
6 ~ 7 |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. Hygroscopic and light sensitive |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 3,Flammability: 0, Reactivity: 1 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
Wikipedia Linking - Bacitracin Google Scholar Search - Bacitracin zinc Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Bacitracin PubChem Compound Summary - Bacitracin zinc Drug Bank - Bacitracin KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Bacitracin http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Bacitracin http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Bacitracin zinc http://mic.sgmjournals.org/ http://www.pnas.org/ http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystalline powder |
| POTENCY | 65IU/mg min (on dried substance base) |
|
SUM OF BACITRACINS |
70.0% min (A,B1,B2, B3) |
| BACITRACIN A |
40.0% min |
|
ZINC |
4.0% ~ 6.0% |
| EARLY ELUTING PEPTIDES |
20.0% max |
| BACITRACIN F | 6.0% max |
| LOSS ON DRYING |
5.0% max |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION | |
|
UN NO. |
Not regulated |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP | |
|
|
| SAFETY INFORMATION |
|
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
May cause allergic skin reaction. Hygroscopic (absorbs moisture from the air). May cause kidney damage. May cause eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation. Target Organs: Kidneys. Eye: May cause eye irritation. Skin: May cause skin irritation. May be harmful if absorbed through the skin. May cause allergic sensitization in certain individuals. Ingestion: May cause irritation of the digestive tract. May be harmful if swallowed. Inhalation: May cause respiratory tract irritation. May be harmful if inhaled. Chronic: May cause kidney damage. |
|
GHS |
|
|
SIGNAL WORD |
Warning |
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
H402 |
|
P STATEMENTS |
|
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|